
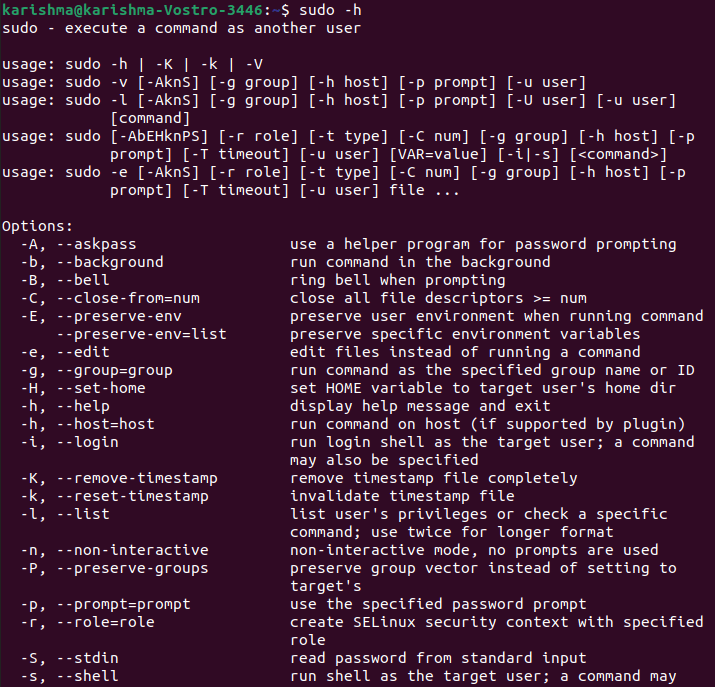
In future posts, we'll look at how sudo can be used to provide more fine-grained options for controlling sudo privileges. > /etc/sudoers: syntax error near line 3 > /etc/sudoers: syntax error near line 3 <<< Fortunately, there are some ways around this that don't involve a lot of work, and the visudo command provides some details on the problems needing to be fixed.
#Full form of sudo in linux password#
password for 5: Fixing a corrupt /etc/sudoers fileĪ corrupt /etc/sudoers file can keep sudo from working and really mess up your day. Extra care should always be taken when using the root account in this way. With a default /etc/sudoers configuration and membership in the sudo (or admin) group, you can assume root control using the command sudo su. There are times when prefacing every command with "sudo" gets in the way of getting your work done. Press to keep the current choice, or type selection number: There are 3 choices for the alternative editor (providing /usr/bin/editor). $ sudo update-alternatives -config editor This command will display a list of editors with the current one marked with an asterisk and allows you to select the one that you prefer. If the editor used by default is one that you’re not comfortable using, you can change it with this command: The /etc/sudoers file should always be modified using the visudo command because this command helps to keep you from causing configuration errors that might make the resultant file unusable (i.e., it can break sudo). Trick 3: Changing the default editor for the visudo command Just use the -u option with the sudo command and specify the username. While most people use sudo access to run commands as root, it also allows you to run commands as other users. Trick 2: Running commands as other users - not just root If you don’t want anyone to have this ability, don’t put anyone in the sudo (or admin) group on your system and this privilege level will not be implemented. The rest of the line allows members of this group to run any command as any user. The $sudo (or %admin) part of this line is a reference to the sudo (or admin) group.
Exclusive for LQ members, get up to 45 off per month. The privileges are derived through a line like this in the /etc/sudoers file: %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL With over 10 pre-installed distros to choose from, the worry-free installation life is here Whether you are a digital nomad or just looking for flexibility, Shells can put your Linux machine on the device that you want to use. If necessary, remove the # character at the beginning of the line: # Defaults targetpw # ask for the password of the target user i.e.Assuming the standard /etc/sudoers setup, they should immediately be able to start using sudo commands once this change has been made. As a Linux system administrator or power. Make sure that the commenting has been removed in the following lines. It stands for super user do and is pronounced like sue dough. Sudoers file maintains by the system administrator, who allows to access rights for some. Open the /etc/sudoers file using the vim editor. sudo command stands for superuser do & also know as sudoers.
#Full form of sudo in linux install#
Localhost:~ # sudo zypper install system-user-mail Localhost:~ # sudo zypper install system-group-wheel To install the packages, enter the following commands: Locate the system-group-wheel and system-user-mail packages. To ensure that your account has this privilege, you must be added to the sudoers file. To assign sudo privileges to a user in Suse Linux, do the following: The sudo privilege is given on a per-user or per-group basis. To check if the change was successful, enter the following command : The sudo command allows an administrator to set up a configuration file called /etc/sudoers and define specific commands that particular users are permitted.

To add the user to this group, enter the following ~]# usermod -aG sudo ~]# usermod -aG sudo jsmith
To assign sudo privileges to a user in Debian and Ubuntu, you must add the user to the sudo group. To check if the change was successful, enter the following command: To add the user to this group, enter the following ~]# usermod -aG wheel ~]# usermod -aG wheel jsmith To assign sudo privileges to a user in CentOS 7, CentOS Stream 8, and CentOS Stream 9, you must add the user to the wheel group. To set the password of the new user, enter the following command: To create a new user, enter the following command: To skip entering this information, press Enter.Ĭhanging the user information for maxmustermannĮnter the new value, or press ENTER for the default Optional: Enter additional user information. To set the password of the new user, enter the following ~]# passwd ~]# passwd johnsmithĮnter the desired password and repeat it. To create a new user, enter the following ~]# adduser ~]# adduser johnsmith

Log in as the root user on the desired server. CentOS 7, CentOS Stream 8, and CentOS Stream 9


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
